How To Write Business Plans and Business Cases
Setting the scene
“What’s the difference between a business case and a business plan?”
Few people can produce a ready answer to that question. After all, both business plans and business cases make predictions about future outcomes, but there is a big difference between the two.
Business plans
are based on the business model or business line of an organisation. They explain how the business will achieve its operational and financial goals by capitalising on the capability of the organisation.
Business plans may be written to explain how a business may meet its growth targets over one or more years.
Business cases
are based on a cost model. Business cases comprise an argument to convince a decision maker to approve a specific course of action over another.
A business case may be produced to justify the purchase of capital equipment.
Contents
4. How long should a business plan be?
5. How should I clarify my ideas?
6. What should a business plan contain?
e) Your proposition – company, product or service
f) Market description, analysis, segmentation, targeting and positioning
g) Explanation of how the product, service or idea is different
i) Outline sales plan and forecast
k) Financials (to include ROI and cash flow)
7. Should I use images and colour?
8. How should I present charts?
13. Structure of a business case
14. How do I encourage a decision?
Business Plan
1. What is a business plan?
A business plan is a written document which describes your business, your goals and how you intend to achieve them over a given period. It is a forecast. It describes your starting point and the strategy you need to reach your proposed end point in one, two or three years.
It details your aims, describes your products and services, analyses market demand, and details the resources you need, the capability you have, and the income you anticipate to generate over a period of time.
In essence, your plan should provide sufficient information for the reader to calculate the credibility of your strategy, your chance of success, and in some cases, the risk people may take by investing in your business.
2. How do I prepare?
Ensure that you can answer questions about your plan with logic, completeness and clear thinking. You need to be able to describe three things:
- The situation – opportunity or problem
- Your plan to address the situation
- The payback
Creating an effective business plan means converting an exciting idea in your head into a compelling story on paper. It means applying logic and reasoning to your thoughts and creating a credible plan of action. Above all, it requires clarity of thought.
Clarity is the connection of your idea – your business proposition – to a coherent set of words, sentences, and numbers. It details what you wish to achieve – the business benefits – the why and who and when and where and how you are going to achieve them.
3. How do I start?
You must be able to answer why people should buy your business, product, service, or idea, in preference to someone else’s. Your answer should include the financial reasons why people should buy from you, which then means that your answer is essentially your value proposition.
A value proposition is a statement of value which you propose to deliver to potential buyers. This should be your starting point for developing your business plan.
Think of your value proposition as your elevator pitch. It should be clear, concise and compelling. It is about how you can deliver greater value or offer a better deal to potential customers than the current market can offer.
A value proposition details how your business, product or service can offer higher quality, lower cost, or something else desired by your customers, that your competitors can neither offer nor replicate easily. A value proposition should comprise a simple set of statements which:
- Describe how your business, product, service, or idea addresses the situation – problem or opportunity.
- Detail why the situation should be addressed or needs to be addressed in terms of opportunity, difficulty, or cost.
- Explain the benefits of your business plan – your business, product, service, or idea over alternatives.
- State the cost advantages of your business, product, service, or idea over competitive alternatives.
4. How long should a business plan be?
A business plan should contain essential information and no more than essential information necessary for the plan. The plan should be as short and as concise as possible. But it must contain everything necessary. In other words, it must be complete and leave no obvious questions unanswered.
A business plan can be as short as a couple of pages to many pages long depending on the product, service, market, and complexity of the proposition.
5. How should I clarify my ideas?
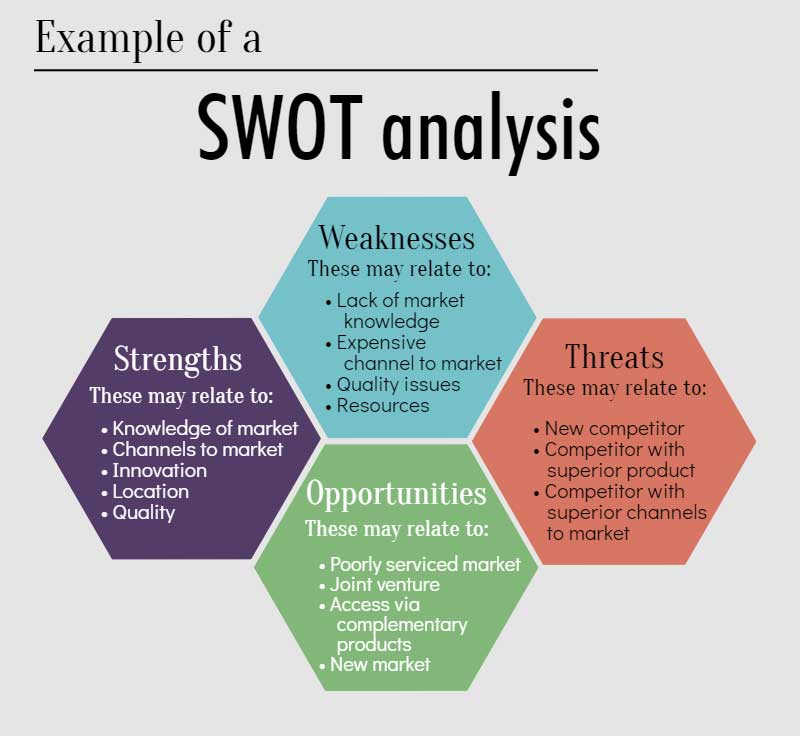
You need to have clarity about all aspects of your business plan and the influences upon it. SWOT may help you to distinguish between unimportant and important aspects which you need to consider. A SWOT analysis is a way of focusing on factors which may influence your success.

In particular, you need to be clear about threats to your plan. Readers need to see that you are knowledgeable about the environment in which you will be trading. That means you should never skip over areas of potential difficulty. Instead, define, analyse and conclude how and why you can overcome them. Realism is desirable in all business plans.
6. What should a business plan contain?
The number of sections your plan needs depends on the focus, technology or complexity of the proposed offering and may include:
a) Executive summary
b) Management profiles (if relevant)
c) Vision statement
d) Mission statement
e) Your proposition – company, product or service
f) Market description, analysis, segmentation, targeting and positioning
g) Explanation of how the product, service or idea is different
h) Outline marketing plan
i) Outline sales plan and forecast
j) Resources
k) Financials (to include ROI and cash flow)
l) How to make it happen
a) Executive summary
The executive summary is the most important part of the document because it is likely to be read by all stakeholders. But don’t think of it as purely a summary of your business plan.
Think of it as an opportunity to “sell” your business idea. Think impact, engagement, and appeal. From your first word to your last, your executive summary requires high energy.
Your first sentence should be a benefit-focused entrée into an appealing, scene setting, first paragraph.
It should detail your vision, mission, the situation, proposal, and payback. It needs to mirror your document in the precise order of your document – from the proposition, market description, considerations, resources required and return on investment to cash flow. It needs to be well-structured, appealing, and highly credible.
Sketch out your executive summary in draft before starting your document. It should represent the skeleton of your document. Produce it in rough before writing your document and complete it after writing your whole document.
An executive summary – over one or perhaps two pages – should have seven parts:
- Proposition summary and how it meets the customer/market needs
- Background
- Situation definition – problem or opportunity
- Approach and proposition
- Financials/costings/payback
- Benefits/rationale to approach
- How to make it happen
b) Management profiles
If the business plan is to secure funding, investors will want to know the capability, experience, and track record of the people who will be driving the business. Short biographies of key people should be detailed.
c) Vision statement
State where you see your business in the future. A vision statement is a high-level overview of the business, the characteristics the business will display, and the goals that it will have achieved by a specific time.
d) Mission statement
Summarise your company’s purpose, means of operation, market, and scope of activity.
e) Your proposition – company, product or service
This section should start with an outline of why you have developed your offering – the need for it – and how it fits within the market, competitively. You should position your company, product or service in the mind of the reader.
The main focus of this section is on what you will offer the market in terms of business, product or service, technically and operationally. You should include charts, diagrams, and images as necessary to enable the reader to understand your offering and its comparative capability.
Ensure that the information you give is complete, that your narrative explains essential details, and that no questions are begged.
f) Market description, analysis, segmentation, targeting and positioning
You should describe your product or service in terms of what marketers call a marketing mix. It’s a means of structuring an offering from a marketing perspective. It comprises: Product, Price, Placement, and Promotion, otherwise known as the 4 Ps.

Product
This is about describing your product range or service, and how you will adapt it to support your customers’ needs and desires.
You should also include guarantees, support, and maintenance. Also include product variation, differentiation, and innovation.
Price
This is the process of setting product prices. It may include discounts which relate to what you think customers are prepared to pay, and how they may wish to pay.
Placement
This might involve distribution channels, direct sales, indirect sales or e-commerce. In essence, you need to detail how you will get your product to market. Don’t go into detail here – instead, give detail at the section on sales plan and forecast.
Promotion
This is about how you will promote your product, product line or company.
Markets are divided into groups of buyers – or segments. You should describe your market in segments.
Tailoring an approach to one or more groups – or one or more segments – over others is the only way to promote your offering. That’s why airlines promote first class services differently from economy class services.
One other thing you need to be aware of is that the segment or segments you propose are valid. Provided that a segment can be identified, is of reasonable size and can be reached economically, then it is a valid marketing target. Here are some variables:
Demographics
These relate to age, gender, income, race, and ethnicity for the purpose of creating a clear and complete picture of the characteristics.
Geography
There are often regional differences. Customer preferences differ depending on which part of the country they may live.
Behaviour
Some customers are brand loyal. Others are heavy users while others are identified as light users.
Psychological/Lifestyle
This is based on activities, interests and opinions.
Segmentation
Segments which should be attractive are those which complement your business’s strengths and where demand, profitability, and growth are favourable.
Identify the variables, and then:
- Group potential customers into segments
- Group products into categories
- Produce Market/Product grid/s
You should also detail market influences. Markets are influenced by a number of factors such as technology, economics, politics, geography, social views, and so on. Refer to your SWOT analysis. You need to identify market factors which may influence your business plan and link them to justify your approach to achieving your proposition.
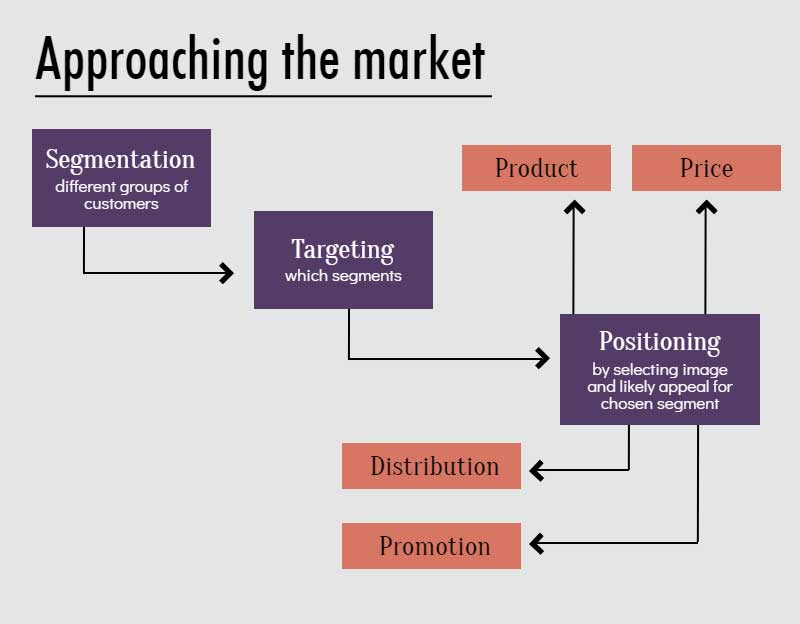
Targeting
Link your marketing mix to your target segment. To do so, you need to answer these questions:
- How well is our target segment served by existing suppliers?
- What would be the cost of reaching that segment?
- How compatible with our strengths is this new target segment?
- What is our competitive position?
- What is the market growth potential?
Positioning
You need to think about how you compare with competitive products and services. You then need to decide how you wish to position your product or service in the eyes of your market.
Positioning is the process by which you create an image or identity in the minds of your target market. It is the “relative competitive comparison” your product or service occupies in a given market – as perceived by the market.
It is about identifying the differential advantage of your business to your target segments. For example, a Rolls Royce Dawn is positioned differently from a Ford Fiesta even though both products are classified as cars.
Your business plan may be focused on an existing product or service or developing something completely new. Alternatively, you may wish to compare what you are offering with a competitive product or service.
g) Explanation of how the product, service or idea is different
Differentiation is about a product, service or idea which is perceived by the market – not purely by you – as being different. Differentiation is the aim of most businesses.
It may relate to lower cost, faster delivery, higher quality, greater adaptability and so on. The aim of differentiation is to match your offering to customer needs, attract your market and generate market advantage. You need to be clear about how you are going to achieve this.
At this point, you should also detail the uniqueness of your offering – your unique selling proposition (USP) – which distinguishes you from the competition.
Think through each element of your offering and link it to the process of getting your offering to market.
h) Outline marketing plan
Produce an outline marketing plan – summarising essential points. Leave full detail to the marketing plan. Digital marketing is likely to play a role in promoting your business, product or service, so you need to detail how it will achieve your goals.
A typical marketing plan includes the following:
Aims
Detail the income the plan is to generate.
Analysis
- Environment – Focus on every external influence on getting your offering to market. It includes economics, social trends, political influences, legal and technological influences. Some factors may be advantageous to you, some not. Whatever they are, you need to detail them.
- Competitors – You need to detail the market positioning of all relevant competitors and their comparative strengths and weaknesses with specific reference to your market.
- Customers.
- Resources.
Objectives
Based on the above analysis.
Positioning strategy
Segmentation, targeting, and positioning.
Marketing mix
The four Ps – Product, Price, Promotion, and Placement.
Proposed marketing activity
Activity is likely to include search engine optimisation (SEO), content marketing, paid advertising (PPC) and social media marketing. Whatever it is that you decide to do, you need to detail it. Produce a chart of proposed activity against forecast return, over time.
Financial targets
Link these through to the financial section of your business plan.
i) Outline sales plan and forecast
The outline sales plan and forecast should include essential sales information from your full sales plan, and nothing more. It should detail the tactics you intend to use to reach your sales goals. If B2B, you should specify the market segments you intend to target and the companies and people you intend to approach.
You need to provide a chart which specifies sales resourcing needs and timescales of the complete sales lifecycle. It should be designed so that it is understood at a glance.
If you have prospects stating an intent to buy, these statements should be included here. The sales plan is the sharp end of your business plan.
The purpose of this section is to give readers confidence by demonstrating realism about your market and credibility about your forecast.
j) Resources
You should detail the resources you need to achieve your business goals – people, time, equipment and money. Specify lead times – recruitment times if relevant – and whatever else you deem essential. Demonstrate how you will achieve what you propose to achieve with the resources you propose to have.
k) Financials
The primary purpose of business, any business, is to make a profit. There is no other primary purpose. For that reason, the methods by which profit will be made needs to be detailed, clear and understandable at a glance
It should be complete and presented simply and clearly, and include:
- Funding requirements, envisaged return on investment, and cashflow.
- Clear description attached to numbers and lines as appropriate.
- Tables and charts with a consistent style.
- Key messages highlighted from each table or chart.
l) How to make it happen
Include a timeline of who has to agree on what and by when.
7. Should I use images and colour?
The answer is yes. Images are a good way of getting points across. If colour makes your proposal look more attractive to read, then use it. Ensure, however, that images and colour support your message and don’t get in the way of it.
8. How should I present charts?
Give your chart a figure number and provide a summary underneath explaining the message your chart conveys. Provide narrative. Never leave it to the reader to interpret what your image or chart might mean.
Business Case
9. What is a business case?
A business case is a justification for a proposed project or plan of action on the basis of its expected commercial benefit. It is a business argument.
It reveals a situation which is either a problem or an opportunity and details how the situation could be addressed in terms of benefits and risks.
It needs to show a compelling case for change, value for money, commercial viability, affordability, and achievability.
10. What is the first stage?
The first stage is to produce a rough justification for addressing a problem or opportunity. It may start with your belief that you can improve a situation, save cost, make money, or achieve competitive advantage.
Whatever it is, you are unlikely to have complete information straight away, but you should have a rough idea.
For instance, you should have an approximate idea of feasibility factors. These may include situation knowledge, market size, competition, income opportunity, costs, funding, resourcing, and risk.
What you should be clear about are the drivers for addressing the situation and why your idea, product or service may have commercial traction. While you might not have complete information, you should have sufficient data to list your anticipated business benefits.
The result of this information is called your value proposition and is the basis of your business case. Refer to section 3 to remind yourself of what a value proposition should contain.
11. How do I test my ideas?
At this stage and at every stage of writing your business case, you need to probe and test your ideas. Great business narrative doesn’t beg questions but answers them, so every one of your statements needs to be supported and credible.
12. Defining options
All options need to be defined, and your analysis needs to be non-controversial. Your analysis should be written in such a way that interested parties would agree with your analysis – even those who are likely to oppose your recommendations.
You should deal with researched facts and not show bias, or reveal recommendations. All reasonable options need to be considered including that of doing nothing (provided that is a reasonable option).
Options need to be detailed in precisely the same way – proposed option, implications, and payback – so that they can be compared equally. Consideration may be:
Strategic
This relates to business synergy and strategic fit. It answers the question whether the option will be good for the overall business.
Economic
This aspect relates to whether it is good value for money.
Commercial
This relates to how the business case will be structured financially and whether it can be considered to be a good deal.
Financial
This is primarily focused on whether the proposal can be funded and is affordable.
Management
This aspect is concerned with whether the preferred option can be delivered successfully as outlined in the business case.
13. Structure of a business case
It should have 7 sections comprising:
- Executive summary
- Purpose
- Problem or opportunity definition
- Proposed business case
- Market analysis
- Financials
- Benefits
Executive summary
This is the most important section of your business case as it is likely to be read by all stakeholders. Produce a benefit-focused first sentence as an entrée into an appealing, scene setting, first paragraph. Your complete summary should be written so that it can be understood at a glance. It should be credible and highly persuasive.
You should draft your executive summary after you have drafted your value proposition but before writing your document. The draft will be approximate and should be finalised after the document has been written.
This section should mirror your document in the precise order of your document – from the proposition, market description, considerations, resources required to the return on investment.
From your first word to your last, your writing requires high energy. It should detail the purpose of your business case, the situation which it addresses, and above all, the benefits of your business case.
Purpose
- Summary of proposed solution.
- Summary of the situation – problem or opportunity.
- Expected outcomes.
- Summary of benefits of proposal solution.
Problem or opportunity definition
Detail the problem or opportunity so that it can be understood at a glance. Your writing should be jargon-free and easily understood by anyone not associated with your business idea.
Your analysis should be non-contentious and utterly factual of the problem or opportunity. It should provide a background and context to your business case and include research data both favourable and unfavourable to your proposition.
Identify all sources of information which contribute towards your proposition. These may include:
Proposed business case
This is the main body of your business case. Your proposition and your approach to the problem or market should be detailed stage by stage. Start with a description of your offering in terms of benefits, features and advantages in that order.
Above all you must explain why your proposition is well-placed to address the situation and precisely how your approach complements your current business strategy.
Three questions your proposition needs to answer at every stage are: How does your idea compare against competitive ideas? How will you reach the market? Where’s the proof that you are likely to succeed?
Anticipate reader questions and answer them within your business case. Provide credibility and proof if possible at every stage.
As a conclusion to this section, you should detail your prospects – or likely users of your proposition or offering – along with their job titles. Readers will be looking for assurance that you really do know your market, can reach it, and are able to generate your forecast financial return.
- Explanation of how the solution addresses the problem or opportunity
- Revenue
- Cost savings
- Non-economic (perhaps relating to regulatory compliance)
Market analysis
If your business case is opportunity focused, then market analysis, competitor analysis and factors related to the selling environment need to be evaluated.
Show complete understanding of the market, and provide a detailed explanation of how you will reach the market.
Strategic fit
Identify which organisational objectives the business case supports and explain how it will support them. (These may include policy, regulatory requirements or commercial governance.)
Assumptions and dependencies
- List assumptions which drive the business case.
- Detail the environment (financial, operational, political or other) on which the solution is dependent.
Competitive analysis
Summarise competitive practices or competitor positioning. If helpful, produce a SWOT analysis.
Alternatives and comparisons
List alternative solutions including “do nothing” provided it’s a realistic alternative.
Next steps
- Timescales for agreement stages.
- Invite questions.
- Summarise and conclude with strong benefit statement.
Financials
This section should provide a cost-benefit analysis detailing the pros and cons of your case. Use facts, figures, and charts to get your messages across and use captions to emphasise them.
Readers need to assimilate critical points from your data at a glance.
- Detail funding requirements, envisaged return on investment, and cash flow.
- Make sure description is attached to numbers and lines as appropriate.
- Ensure every table and chart has a consistent style.
- Highlight key messages from each table or chart.
Benefits
List the benefits in order of importance. These should relate to all considerations from the financial to the strategic.
14. How do I encourage a decision?
Specify the critical path – a timeline – of all stages of approval necessary to proceed. Include the names of the people who need to give their approval.
15. Any winning tips?
Once you’ve checked the coherence of your argument and the completeness of your document, it is time to cast a critical eye. In addition to being complete, your document needs to look highly readable.
Make sure that your proposition is business-appealing, logical, strong, well-written and with all essential facts and figures.
Ensure your document is clear, complete, and looks good. Appearance is important. Something which looks good is likely to be read. Masses of text is unappealing. Short paragraphs and clear structure is appealing. Ensure that essential information can be read at a glance.
16. One last thing…
Mistakes in spelling, punctuation or grammar not only distract but reduce the credibility of your document. Ask others to proofread. Then check and recheck before submitting what will become your highly effective business case.
This blog was written by Richard Walker, a director of Walkerstone Limited.
He can be contacted at: richard@walkerstone.com
Walkerstone comprises business case writers, proposal writers and professional trainers.
We delivery scheduled courses, in-company training and executive coaching to people and organisations throughout Europe.
Courses include:
Business Case Writing
Essential Business Writing Skills
Presentation Skills
Proposal Writing
Report Writing
If you would like to know more, do contact us. We’d be delighted to hear from you.
Email: hello@walkerstone.com
Telephone: 01252 792 270
Discover More
Boost your skills quickly, easily, and affordably with our brand-new online video course, Mastering the Art of Essential Business Writing, available for just £49.
Designed with your success in mind, this course covers everything from foundational principles and grammar essentials to advanced techniques such as crafting compelling executive summaries.
You’ll master the power of words, sharpen your reasoning and logic, and learn how to persuade and summarise effectively. You’ll achieve the ability to:
- · Engage because of your improved level of grammar, punctuation, and writing technique.
- · Communicate effectively because of your ability to present information with logic and reasoning.
- · Craft documents from polished emails to highly readable plans and reports.
- · Persuade by deploying effective literary techniques.
Need Tutor Guidance?
We make learning effortless. You can book a personal tutor for one-on-one guidance for 30-minute sessions via Teams.
Interactive Learning
This course goes beyond theory with practical exercises and quizzes designed to reinforce your knowledge:
- · Quizzes: Test your understanding after each module to ensure you’re on track.
- · Hands-On Exercises: Apply your skills in realistic business scenarios to gain practical experience.
Flexible Learning
Study at your own pace from anywhere in the world. Whether you’re aiming to enhance your daily communication or elevate your business writing, this course is tailored to meet your needs.